Abgeschlossene Projekte
Der Lehrstuhl für Geoinformatik hat bereits eine Vielzahl an Projekten erfolgreich abgeschlossen. Mehr Informationen über jedes Projekt finden Sie auf den einzelnen Projektseiten.
Future Cities Pilot

The "Future Cities Pilot" (FCP), an initiative by Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC), aims at demonstrating and enhancing the ability of spatial data infrastructures to support quality of life, civic initiatives and urban resilience. The first phase of this pilot project (termed FCP1) is based in Europe and is sponsored by Ordnance Survey Great Britain, Institut National de l'Information Géographique et Forestière (IGN) France, city of Sant Cugat del Vallès (Barcelona), Spain and virtualcitySYSTEMS GmbH Berlin and in collaboration with buildingSMART International (bSI). The objective of the OGC pilot project is to demonstrate how use of, international standards such as CityGML and IFC together can provide stakeholders with information, knowledge and insight which enhances financial, environmental, and social outcomes for citizens living in cities. Results from this initiative will be documented in Engineering Reports (ERs) in the context of a hands-on engineering experience. This initiative is aimed to develop, test, identify gaps and demonstrate the use of these technologies in a real world-type scenario developed in collaboration with the sponsors. The final demonstrations will be presented in Smart City Expo in Barcelona in November, 2016. [more...]
Semantisches 3D-Landschaftsmodell Vorarlberg (VoDLM3D)

Die Nachfrage an dreidimensionalen Stadt- und Landschaftsmodellen steigt stetig. So werden diese beispielsweise für Standortanalysen oder Simulationen von Naturgefahren verwendet. Für viele Anwendungsfälle sind dabei neben der rein visuellen Darstellung auch die semantischen Informationen der Objekte relevant. Zu diesem Zweck wurde an der TUM ein Pilotprojekt in Kooperation mit dem Land Vorarlberg und der Firma virtualcitySYSTEMS (VCS) gestartet, das als Ziel die Erzeugung eines semantisch auswertbaren dreidimensionalen digitalen Landschaftsmodells hat. [mehr...]
3D Tracks
Die DFG-Forschergruppe "Rechnergestützte kooperative Trassenplanung in mehrskaligen 3D-Stadt- und Bauwerksmodellen" hat zum Ziel Methoden und Techniken zur kooperativen Planung von Infrastrukturbauwerken zu erforschen und zu entwickeln. An dem Projekt sind fünf Gruppen an der Technischen Universität München sowie dem Karlsruher Institut für Technologie beteiligt. [mehr...]
Geodatenpool Bodensee
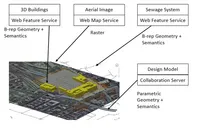
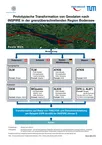
Von den Vermessungsverwaltungen Baden-Württembergs, Bayerns, Österreichs und der Schweiz wurde ein Pilotprojekt initiiert, mit dem Ziel, topographische Daten und Katasterdaten prototypisch mittels semantischer Transformation in die INSPIRE-Datenmodelle aus Anhang I der INSPIRE-Richtlinie zu überführen und über Darstellungs- und Downloaddienste bereitzustellen. Die semantische Transformation wird dabei anhand zweier unterschiedlicher Ansätze erprobt, dem formatbasierten Ansatz sowie dem modellbasierten Ansatz. [mehr...]
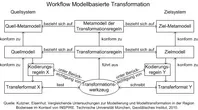
Modellbasierter Ansatz für den Web-Zugriff auf verteilte Geodaten am Beispiel grenzübergreifender GIS-Anwendungen (mdWFS)
Im Rahmen des Projekts wird ein Lösungsansatz zur webbasierten Modelltransformation von Geodaten entwickelt. Er beinhaltet die Spezifikation einer konzeptionellen Sprache zur Formulierung von Modellabbildungsregeln für semantische Transformationen sowie die Spezifikation einer Schnittstelle für einen modellbasierten Web Service mit der Fähigkeit zur semantischen Transformation. [mehr...]
Prototypische Enwticklung Mobiler Anwendungen im Kontext von INSPIRE und COPERNICUS (InGeoSat 2)
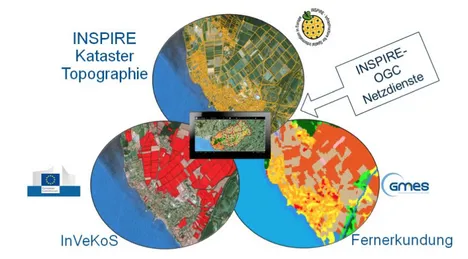
Ziel dieses Projekts ist die Entwicklung einer prototypischen Anwendung auf Basis einer mobilen GIS-Plattform. Unter dem Android Betriebssystem wird eine native Android-Applikation implementiert, mit welcher primär INSPIRE, COPERNICUS und InVeKoS-Daten visualisiert werden. Zudem besteht die Möglichkeit über standardisierte OGC- und INSPIRE-Webdienste externe Geodaten einzuladen. Die Potentiale der mobilen Plattform werden anhand einfacher Funktionalitäten der Applikation aus den Bereichen Flurbereinigung, Kataster und Landnutzung sowie der Kombination von INSPIRE- Datenstrukturen mit Fernerkundungsdaten (COPERNICUS) und Landnutzungsdaten (InVeKoS) aufgezeigt. [mehr...]
Modeling City Systems - A Platform-based Approach for Climate-aware Integrated City Plannig and Management
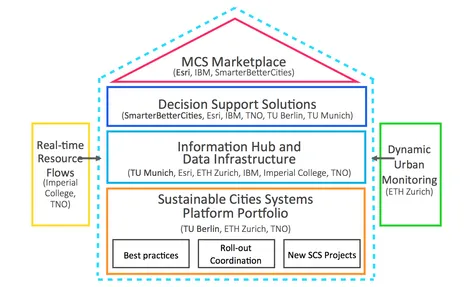
In addressing the challenges to meet the 2050 Greenhouse Gas reduction targets for Europe coupled with the aspirations to improve sustainability and liveability, it is critical that city planners, developers and decision-makers have the capacity to understand how city systems operate, how they interact, and what impact changes to systems has on the system itself and other interacting systems. The growing complexity of city systems and the added complexity of external and growing pressures means that solutions which model, analyse, and help to operationalize systems are more needed than ever before, and inherently require a greater degree of sophistication than ever before. This project builds on the work of the Sustainable City Systems Platform, which has identified urban design, planning and management solutions as one of the biggest opportunity areas for the Climate-KIC and therefore one of three priority areas for 2014. [mehr...]
VerNet-LEM

Ziel des Projekts ist es, eine kleinräumige, wetterabhängige Prognose für die Einspeiseleistung und den Verbrauch zu erstellen und damit die Kompatibilität der Rechenressourcen mit den im Verteilnetz installierten Komponenten und Leitungen zu bewerten. In einem weiteren Schritt werden die zu ergreifenden Maßnahmen simuliert und bewertet. Abschließend wird ein Prognose- und Simulationssystem entwickelt, mit dem Netzbetreiber den Betrieb in Verteilnetzen optimieren können.[mehr...]
Indoor Navigation with different Locomotion Types
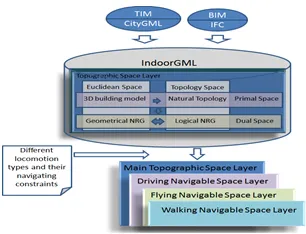
The purpose of this project is to support different types of locomotion for indoor navigation through determining safe navigable subspaces for each type of locomotion namely flying, walking, and driving using semantically enriched 3D building models. The subspaces are computed using geometrical-based method i.e., configuration space. The whole subspacing procedure is carried out in Multilayered Space-Event Model (MLSEM). MLSEM is a framework which is based on sound mathematical rules and provides application schema i.e., IndoorGML.[mehr...]